Portfolio item number 1
Short description of portfolio item number 1
Short description of portfolio item number 1
Short description of portfolio item number 2 
Published in ACM MultiMedia, 2015
This project provides the first deep crowd counting work with negative sampling, and presents a new dataset with large counting range.

Published in IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2017
We present a new object co-segmentation framework, which takes advantages of semantic information and globally explores multiple co-occurring matching cliques based on an N-partite graph structure.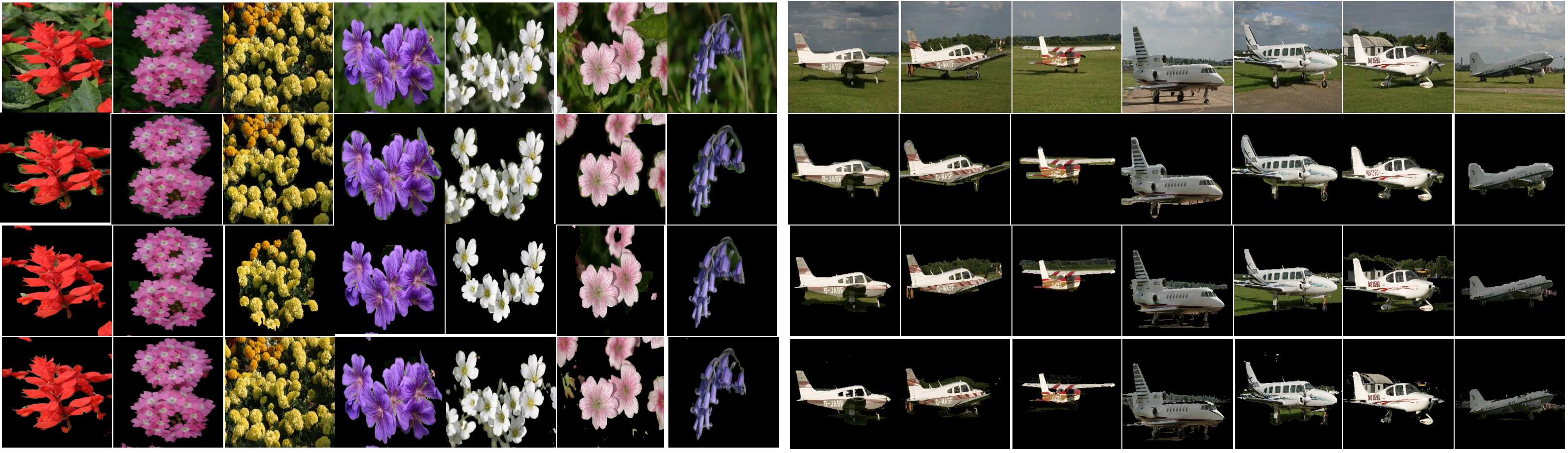
Published in IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2020
We address the corresponding text detection task and propose a novel text co-detection method to identify the co-occurring texts among multi-view scene images with compositions of detection and correspondence under large environmental variations.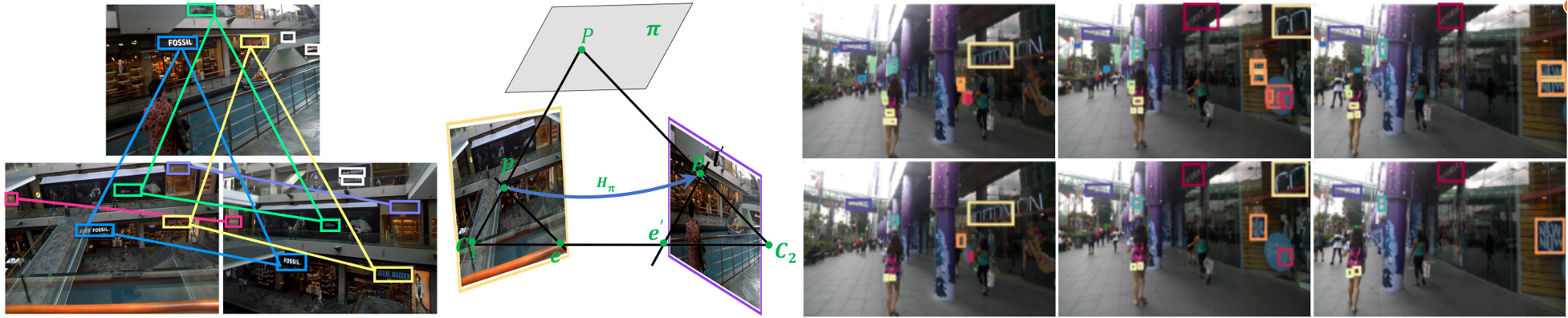
Published in AAAI, 2021
In this paper, we aim at providing a novel explanation to the question of “Why do attributes propagate in GCNNs?”, which not only gives the essence of the oversmoothing, but also illustrates why the GCN extensions, including multiscale GCN and GCN with initial residual, can improve the performance.
Published in AAAI, 2022
In this project, a novel Diverse and Interactive Message Passing (DIMP) is proposed for self-supervised learning by overcoming over-smoothing in semi-supervised learning.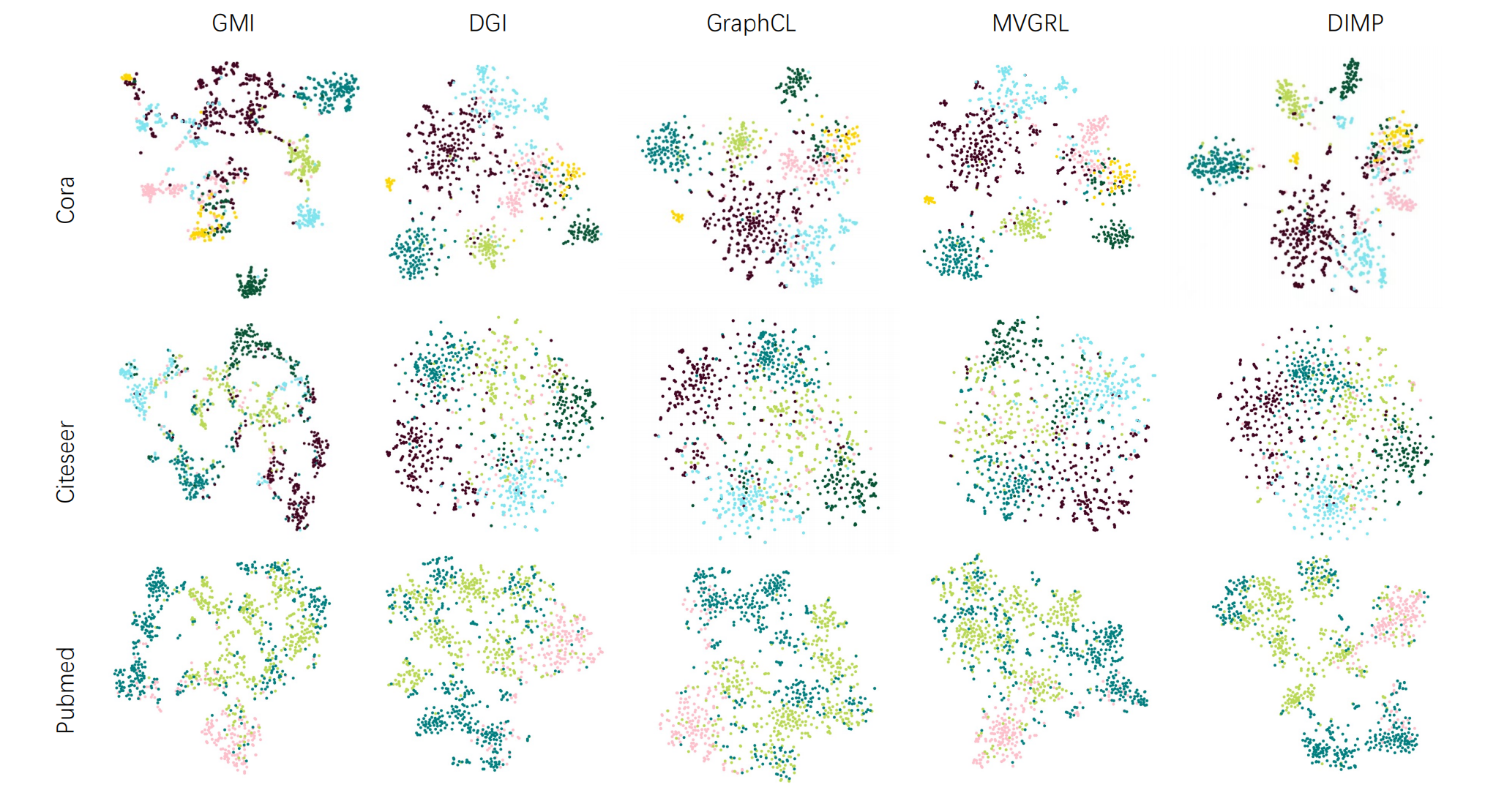
Published in ICASSP, 2022
In this project, we revisit the visual context propagation in SGG and propose a Progressive Message Passing Network to estimate context in a coarse-to-fine manner.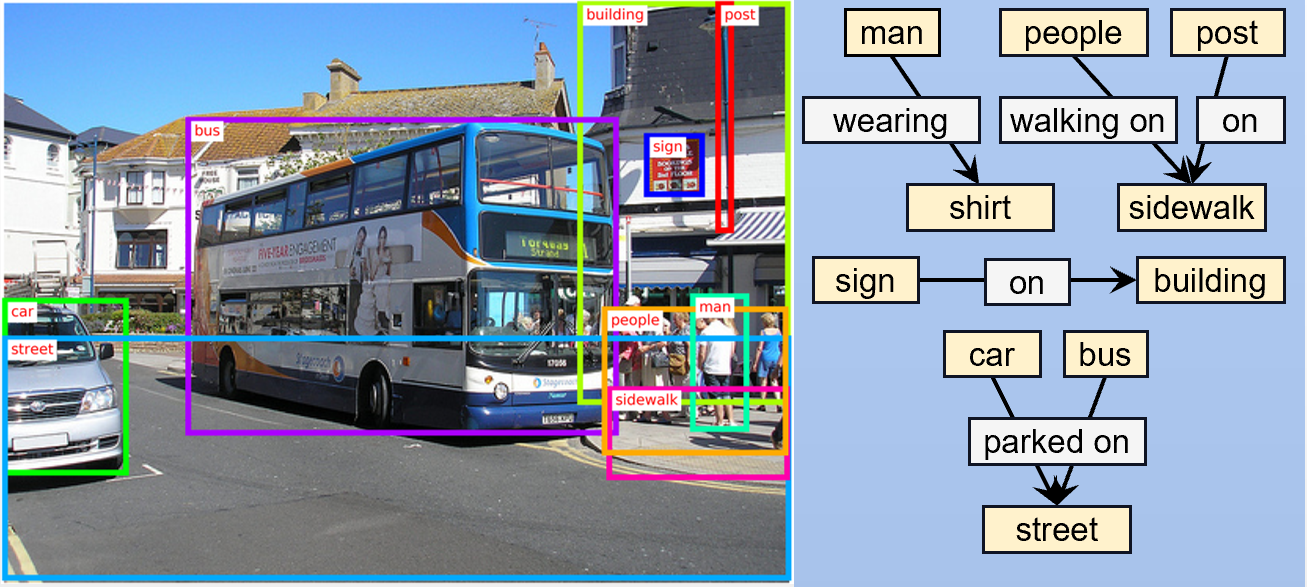
Download here
Published in ICASSP, 2023
The short video has gained increasing attention in information sharing and commercial promotions due to the fast development of social platforms. Accompanying, it introduces great requirements for assessing the quality of short videos for efficient information acquirement and propagation. However, existing video quality assessment researches focus on assessing video content with five rating scores, limiting the assessment to a one-dimension and simplified criterion. In this paper, we establish a novel database dubbed MMSVD-Douyin for assessing multi-modal short video quality under consideration of three evaluation criteria. It includes 4,684 short videos, three kinds of modalities, six kinds of data formats, and three assessment criteria. To conduct the short video quality assessment, we set up an all-around multi-modal short video quality assessment benchmark (MulSVQA) that dynamically fuses representations from three modalities and produces numbers of ”likes”, ”shares” and ”comments” of short videos.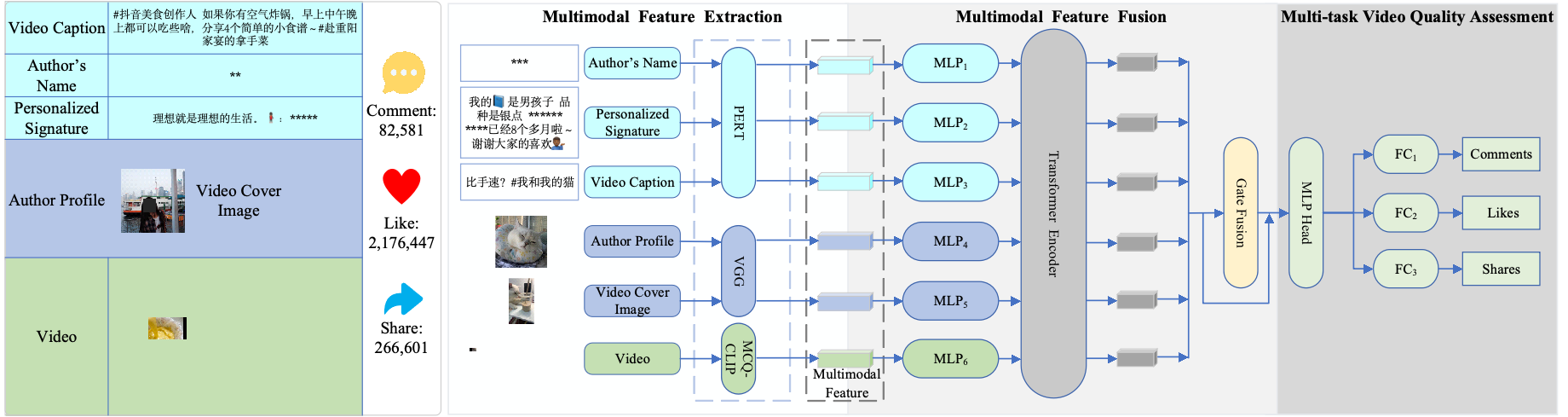
Download here
Published in ACM MM, 2023
Panoptic Scene Graph Generation (PSG) presents pixel-wise instance detection and localization, leading to comprehensive and precise scene graphs. To alleviate insufficient training caused by incomplete segmentation and proposal extraction, we construct a novel twostage framework for the PSG problem. In the training phase, we design a proposal matching strategy, which replaces deterministic segmentation results with proposals extracted from the off-theshelf panoptic head for label alignment, thereby ensuring the allmatching of training samples. In the inference phase, we present an innovative concept of employing relation predictions to constrain segmentation and design a relation-constrained segmentation algorithm. The algorithm recovers more valid instances and predicts more complete scene graphs by reconstructing the process of generating segmentation results from proposals using predicted relation results.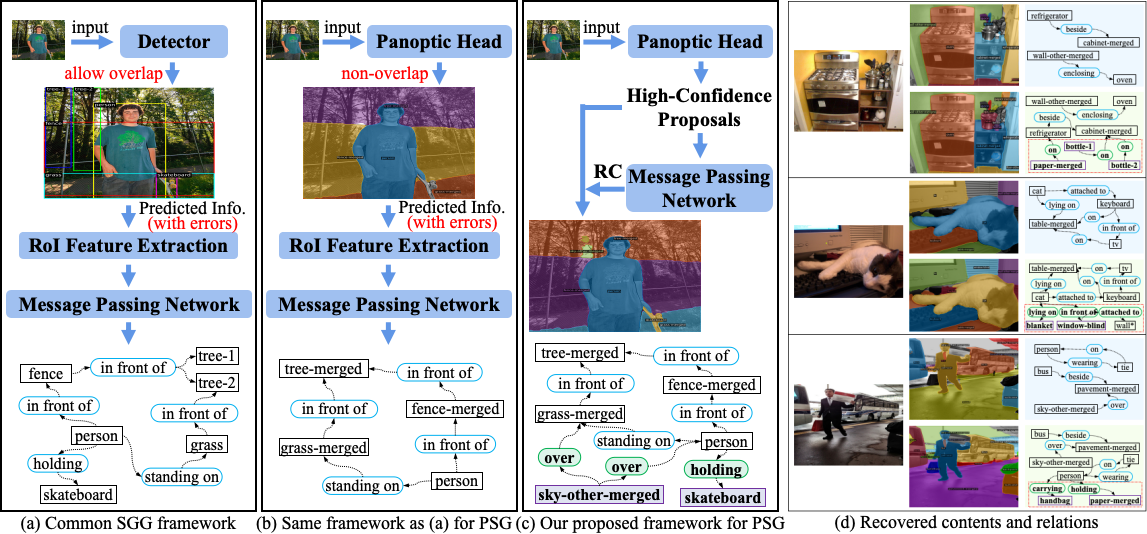
Download here
Published in IEEE TIP, 2024
Scene Graph Generation (SGG) aims to detect all objects and identify their pairwise relationships in the scene. Recently, tremendous progress has been made in exploring better context relationship representations. Previous work mainly focuses on contextual information aggregation and uses de-biasing strategies on samples to eliminate the preference for head predicates. However, there remain challenges caused by indeterminate feature training. Overlooking the label confusion problem in feature training easily results in a messy feature distribution among the confused categories, thereby affecting the prediction of predicates. To alleviate the aforementioned problem, in this paper, we focus on enhancing predicate representation learning. In this project, we provide an effective and general solution, termed AMP-BiC, from the view of feature learning for complex scene graph understanding. AMP-BiC simultaneously achieves both the discriminated information propagation and aggregation during message passing and the de-confusion and de-bias during training.</p>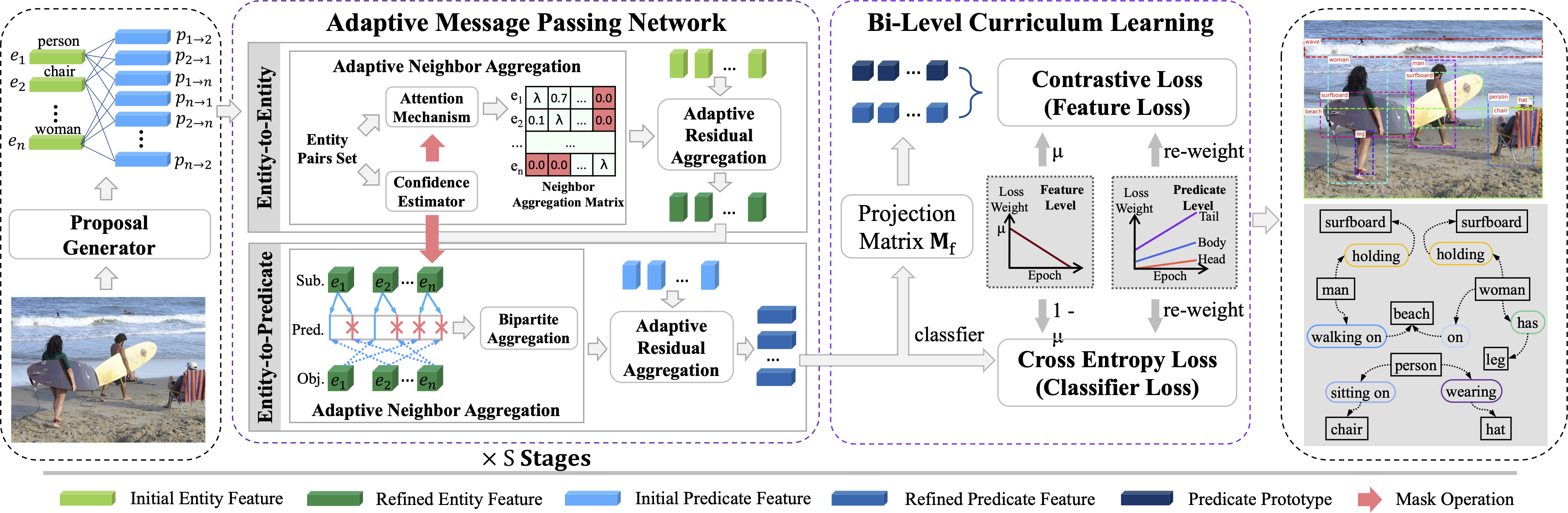
Published:
This is a description of your talk, which is a markdown files that can be all markdown-ified like any other post. Yay markdown!
Published:
This is a description of your conference proceedings talk, note the different field in type. You can put anything in this field.
Undergraduate course, University 1, Department, 2014
This is a description of a teaching experience. You can use markdown like any other post.
Workshop, University 1, Department, 2015
This is a description of a teaching experience. You can use markdown like any other post.